A
Acceptance Error, Beta Error, Type II Error - An error made by wrongly accepting the null hypothesis when the null is really false.
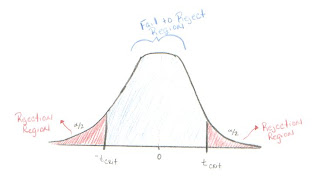
Acceptance Region - Opposite of the Rejection Region. It is better to call this the "Fail to Reject Region." In the case of a two-tailed hypothesis t-test, it is shaded in light blue on the picture below. If the test statistic falls between -t
critical and t
critical then we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Adjusted R-Squared, R-Squared Adjusted - A version of R-Squared that has been adjusted for the number of predictors in the model. R-Squared tends to over estimate the strength of the association especially if the model has more than one independent variable.
Alpha [A, a ], Chosen Significance Level - The maximum amount of chance a statistician is willing to take that they will do not accept a null hypothesis that is true (Type I Error).
Alpha Error, Type I Error - An error made by wrongly rejecting the null hypothesis when the null is really true.
Alternative Hypothesis, Research Hypothesis - An hypothesis that does not conform to the one being tested, usually the opposite of the null hypothesis. Symbolized.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) - A test of differences between mean scores of two or more groups with one or more variables.
Approximation Curve, Curve Fitting - the general method for using a line or curve to estimate the relationship between two associated numerical variables.
Autocorrelation - This occurs when later variables in a time series are correlated with earlier variables.
B
Backward Elimination - A method of determining regression equation that starts with a regression equation that includes all independent variables and then remover variables that are not useful one at a time
Best Subsets Regression - A method of determining the regression equation used with statistical computer applications that allows the user to run multiple regression models using a specified number of independent variables. The computer will sort through all of the models and display the "best" subsets of all the models that were run. "Best" is typically identified by the highest value of R-squared. Other diagnostic statistics such as R-square adjusted and Cp are also displayed to help the user determine their best choice of a model.
Bell-Shaped Curve - A symmetrical curve. Looks like the cross-section of a bell.
Best Fit, Goodness of Fit - A model that is the best model for the given data.
Beta Error, Acceptance Error, Type II Error - An error made by wrongly accepting the null hypothesis when the null is really false.
Bivariate Association/ Relationship - The relationship between two variables only.
C
Cp Statistic - Cp measures the differences of a fitted regression model from a true model, along with the random error. When a regression model with p independent variables contains only random differences from a true model, the average value of Cp is (p+1), the number of parameters. Thus, in evaluating many alternative regression models, our goal is to find models whose Cp is close to or below (p+1).
Cook’s Distance: Cook’s distance combines leverages and studentized residuals into one overall measure of how unusual the predictor values and response are for each observation. Large values signify unusual observations. Geometrically, Cook’s distance is a measure of the distance between coefficients calculated with and without the ith observation. Cook and Weisberg suggest checking observations with Cook’s distance > F (.50, p, n-p), where F is a value from an F-distribution.
Coefficient of Determination – In general the coefficient of determination measures the amount of variation of the response variable that is explained by the predictor variable(s). The coefficient of simple determination is denoted by r-squared and the coefficient of multiple determination is denoted by R-squared.
Coefficient of Variation – The coefficient of variation, in regression, is the standard deviation of the predictor variable divided by the mean of the predictor variable. If this value is small, your variation in the y-values (predictor values) is nearly constant. This implies that the data are ill-conditioned.
Confidence Bands (Upper & Lower) - This is the range of the responses that can be expected for all of the appropriate inputs of X's. The upper confidence band is the highest value that the ÿh value is predicted to be. The lower confidence band is the lowest value predicted that ÿh could be.
Confidence Level - This is the amount of error allowed for the model (given as a percent or a).
Confidence Intervals - A range of values to estimate a value of a population parameter. Associated with the range of values is also the amount of confidence the researcher has in the estimate. For example, we might estimate the cost of a new space vehicle to be 35 million dollars. Assume that the confidence level is 95% and the margin of error is 5 million dollars. We say that we are 95% confident that the cost is between 30 and 40 million dollars.
Confidence Interval Bounds, Upper and Lower - The lower endpoint on a confidence interval is called the lower bound or lower limit. The lower bound is the point estimate minus the margin of error. The upper bound is the point estimate plus the margin of error.
Correlation - The amount of association between two or more items. In these tutorials, correlation will refer to the amount of association between two or more numerical variables.
Correlation Coefficients, Pearson’s Sample Correlation Coefficient, r - Measures the strength of linear association between two numerical variables.
Correlation Matrix - A table that shows all pairs of correlations coefficients for a set of variables.
Correlation Ratio- A kind of correlation used when the relation between two variables is assumed to be curvilinear (i.e. not linear).
Curve Fitting, Approximation Curve - the general method for using a line or curve to estimate the relationship between two associated numerical variables.
D
Degrees of Freedom, df, - The number of values that can vary independently of one another. For example, if you have a sample of size n that is used to evaluate one parameter, then there are n-1 degrees of freedom.
Dependent Variable, Response Variable, Output Variable - The variable in correlation or regression that cannot be controlled or manipulated. The variable that "depends" on the values of one or more variables. In math, y frequently represents the dependent variable.
DFITS, DFFITS: Combines leverage and studentized residual (deleted t residuals) into one overall measure of how unusual an observation is. DFITS is the difference between the fitted values calculated with and without the ith observation, and scaled by stdev (Ŷi). Belseley, Kuh, and Welsch suggest that observations with DFITS >2Ö(p/n) should be considered as unusual
Dummy Variable, Indicator Variable - A variable used to code the categories of a measurement. Usually, 1 indicates the presence of an attribute and 0 indicates the absence of an attribute. Example: If the measurement variable is cost of space flight vehicle then the vehicle might be manned or unmanned. Let the dummy variable be 1 if the vehicle is manned and 2 if it is unmanned. Note: Dummy variable coding can be used for more than 2 categories.
E
Efficiency, Efficient Estimator - It is a measure of the variance of an estimate's sampling distribution; the smaller the variance, the better the estimator.
Error - In general, the error difference in the observed and estimated value of a parameter.
Errors, Residuals - In regression analysis, the error is the difference in the observed Y values and the predicted Y values that occur from using the regression model. See the graph below.
Error, Specification (Specification error) - A mistake made when specifying which model to use in the regression analysis. A common specification error involves including a irrelevant variable and leaving out an important variable.
F
F (F test statistic) - This is the test statistic for whenever conducting an analysis of variance.
Fits, Fitted Values, Predicted Values - The Fits are the predicted values found by substituting the original values for the independent variable(s) into the regression equation. The name "fit" refers to how well the observed data matches the relationship specified in the model.
Forward Selection - A frequently available option of statistical software applications. A method of determining the regression equation by adding variables to the regression equation until the addition of new variables does not appear to be worthwhile.
F-test: An F-test is usually a ratio of two numbers, where each number estimates a variance. An F-test is used in the test of equality of two populations. An F-test is also used in analysis of variance, where it tests the hypothesis of equality of means for two or more groups. For instance, in an ANOVA test, the F statistic is usually a ratio of the Mean Square for the effect of interest and Mean Square Error. The F-statistic is very large when MS for the factor is much larger than the MS for error. In such cases, reject the null hypothesis that group means are equal. The p-value helps to determine statistical significance of the F-statistic.
G
General Linear Model (GLM) - A full range of methods used to study linear relations between one continuous dependent variable and one or more independent variables, whether continuous or categorical. “General” means the kind of variable is not specified. Examples include Regression and ANOVA.
H
Heteroscedasticity - Non constant error variance. Hetero = different; scedasticity = tendency to scatter.
Hierarchical Regression Analysis - A multiple regression analysis method in which the researcher, not a computer program, determines the order that the variables are entered into and removed from the regression equation. Perhaps the researcher has experience that leads him/her to believe certain variables should be included in the model and in what order.
Homoscedasticity - Constant error variance. Homo = same; scedasticity = tendency to scatter.
Hypothesis Testing - This is the common approach to determining the statistical significance of findings.
I
Independent Variable, Explanatory Variable, Predictor Variable, Input Variable - The variable in correlation or regression that can be controlled or manipulated. In math, x frequently represents the independent variable.
Influential Observation - An observation that has a large effect on the regression equation. Note: Outliers and leverage points may be influential observations, but influential observations are usually outliers and leverage points.
Intercorrelation - Correlation between variables that are all independent (no dependent variables involved).
L
Least Squares Regression - Regression analysis method which minimizes the sum of the square of the error as the criterion to fit the data. This can refer to linear or curvilinear regression.
Leverages, Leverage Points - An extreme value in the independent (explanatory) variable(s). Compared with an outlier, which is an extreme value in the dependent (response) variable.
Linear Correlation- A relationship between the independent and dependent data, that whenever plotted forms a straight line.
Linear Regression - Typically when regression is used without qualification, the type of regression is assumed to be linear regression. This is the method of finding a linear model for the dependent variable based on the independent variable(s).
M
Mean Square Residual, Mean Square Error (MSE) - A measure of variability of the data around the regression line or surface.
Measurement Error (Error, Measurement) - inaccurate results due to flaw(s) in the measuring instrument.
Multicollinearity, Collinearity - The case when two or more independent variables are highly correlated. The occurrence of multicollinearity can cause difficulties in multiple regression. If the independent variables are interrelated, then it may be difficult or impossible to find the specific effect of only one independent variable.
Multiple Correlation Coefficient, R - A measure of the amount of correlation between more than two variables. As in multiple regression, one variable is the dependent variable and the others are independent variables. The positive square root of R-squared.
Multiple Correlation - Correlation with one dependent variable and two or more independent variables. Measures the combined influences of the independent variables on the dependent. gives the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable that can be explained by the action of all the independent variables taken together.
Multiple Correlation Matrices - A table of correlation coefficients that shows all pairs of correlations of all the parameters with in the sample.
Multiple Correlation Plots - A collection of scatterplots showing the relationship between the variables of interest.
Multiple R - That is the name MS Excel uses for the Multiple Correlation Coefficient, R.
Multiple Regression, Multiple Linear Regression - A method of regression analysis that uses more than one independent (explanatory) variable(s) to predict a single dependent (response) variable. Note: The coefficients for any particular explanatory variable is an estimate of the effect that variable has on the response variable while holding constant the effects of the other predictor variables. “Multiple” means two or more independent variables. Unless specified otherwise, “Multiple Regression” generally refers to “Linear” Multiple Regression.
Multiple Regression Analysis (MRA) - Statistical methods for evaluation the effects of more than one independent variable on one dependent variable.
N
Negative Correlation- This occurs whenever the independent variable increases and the dependent variable decreases. This is also called a negative relationship.
Nonadditivity - A statement used to describe a relation when the addition of the separate effects do not add up to the total effect.
Nonlinearity - The events are not the same as their causes.
Nonlinear Relationship - A relationship between two variables for which the points in the corresponding scatterplot do not fall in approximately a straight line. Nonlinearity may occur because there is not a defined relationship between the variables as in the first figure below, or because there is a specific curvilinear relationship. See the parabolic relationship shown in the second graph below.
Normality Plot, Normal Probability Plot - A graphical representation of a data set used to determine if the sample represents an approximately normal population. A graph from Minitab is shown below. The sample data is on the x-axis and the probability of the occurrence of that value assuming a normal distribution is on the y-axis. If the resulting graph is approximately a straight line, then the distribution is approximately normal. There are statistical hypothesis tests for normality as well.
Null Hypothesis, - This is the hypothesis that two or more variables are not related and the researcher wants to reject.
O
Outlier - An extreme value in the dependent (response) variable. Compared with a leverage point, which is an extreme value in the independent (explanatory) variables.
P
Partial Correlation - Correlation between two variables given that the linear effect of one or more other variables has been controlled. Example. r12.3 is the correlation of variables one and two given that variable three has been controlled.
Partial Correlation Coefficients - This is the square root of a coefficient of partial determination. It is given the same sign as that of the corresponding regression coefficient in the fitted regression function.
Partial Determination Coefficients- This measures the marginal contribution of one X variable when all others are already included in the model. In contrast, the coefficient of multiple determination, , measures the proportion reduction in the variation of Y achieved by the introduction of the entire set of X variables considered in the model.
Partial Regression Coefficient, Partials - In a multiple regression equation, the coefficients of the independent variables are called partial regression coefficients because each coefficient tells only how the dependent variable varies with the selected independent variable.
Pearson’s Sample Correlation Coefficient, r - Measures the strength of linear association between two numerical variables.
Population - A group of people that one whishes to describe or generalize about.
Predictor Variable, Independent Variable, Explanatory Variable, Input Variable - The variable in correlation or regression that can be controlled or manipulated. In math, x frequently represents the independent variable.
Prediction Equation - An equation that predicts the value of one variable on the basis of knowing the value of one or more variables. Note: Formally prediction equation is a regression equation that does not include an error term.
Prediction Interval - In regression analysis, a range of values that estimate the value of the dependent variable for given values of one or more independent variables. Comparing prediction intervals with confidence intervals: prediction intervals estimate a random value, while confidence intervals estimate population parameters.
Population Parameter, Parameter - A measurement used to quantify a characteristic of the population. Even when the word population is not used with parameter, the term refers to the population. Example: The population mean is a measure of central tendency of the population. The population parametric is usually unknown.
Proportional Reduction of Error (PRE) - A measure of association that calculates how much more you can reduce your error in the predication of y if you know x, then when you do not know x. Pearson’s r is not a PRE, but r-squared is a PRE.
Positive Correlation- This relationship occurs whenever the dependent variable increases as the independent variable increases
P-values, Observed Significance Level - The probability of making a Type I error. (i.e. given that the null is true, the probability of getting a data set like the one we have or one more extreme in the direction of the alternative.)
R
r, Correlation Coefficients, Pearson’s r - Measures the strength of linear association between two numerical variables.
R, Coefficient of Multiple Correlation - A measure of the amount of correlation between more than two variables. As in multiple regression, one variable is the dependent variable and the others are independent variables. The positive square root of R-squared.
r2 , r-squared (r-sq.), Coefficient of Simple Determination - The percent of the variance in the dependent variable that can be explained by of the independent variable.
R-squared, Coefficient of Multiple Determination - The percent of the variance in the dependent variable that can be explained by all of the independent variables taken together.
R-Squared Adjusted (R-sq. adj.), Adjusted R-Squared - A version of R-Squared that has been adjusted for the number of predictors in the model. R-Squared tends to over estimate the strength of the association especially if the model has more than one independent variable.
Range of Predictability, Region of Predictability - The range of independent variable(s) for which the regression model is considered to be a good predictor of the dependent variable. For example, if you want to predict the cost of a new space vehicle subsystem based on the weight, and all of the input data subsystem weights all range from 100 to 200 pounds. You could not expect the resulting model to provide good predictions for a subsystem that weighs 3000 pounds.
Regression Analysis, Statistical Regression, Regression - Methods of establishing an equation to explain or predict the variability of a dependent variable using information about one or more independent variables. The equation is often represented by a regression line, which is the straight line that comes closest to approximating a distribution of points in a scatter plot. When "regression" is used without any qualification it refers to “linear” regression.
Regression Artifact, Regression Effect - An artificial result due to statistical regression or regression toward the mean.
Regression Coefficient, Regression Weight - In a regression equation the number in front of an independent variable. For example, if the regression equation is Y = mx + b then m is the regression coefficient of the x-variable. The regression coefficient estimates the effect of the independent variable(s) on the dependent variable. (Compare with Partial Regression Coefficients)
Regression Constant - Unless specified otherwise, the regression constant is the intercept in the regression equation.
Regression Equation - An algebraic equation that models the relationship between two (or more) variables. If the equation is Y = a + bX + e, then Y is the dependent variable, X is the independent variable, b is the coefficient of X, and a is the intercept, and e is the error term (See Prediction Equation).
Regression Line, Trend Line - When the best fitting regression model is a straight line, that line is called a regression “line.” Ordinary Least Squares method is usually used for computing the regression line.
Regression Model - An equation used to describe the relationship between a continuous dependent variable, an independent variable or variables, and an error term.
Regression Plane - When the regression model has two independent variables, then a plane represents the relationship between the variables two-dimensional. Example: z = a + bx + cy
Regression SS (also SSR or SSregression) - The sum of squares that is explained by the regression equation. Analogous to between-groups sum of squares in analysis of variance.
Regression Toward the Mean - The type of bias described by Francis Galton, a 19th century researcher. A tendency for those who score high on any measure to get somewhat lower scores on a subsequent measure of the same thing- or, conversely, for someone who has scored very low on some measure to get a somewhat higher score the next time the same thing is measured. Knowing how much regression toward the mean there is for a particular pair of variables gives you a prediction. If there is very little regression, you can predict quite well. If there is a great deal of regression, you can predict poorly if at all.
Regression Weight, Regression Coefficient - In a regression equation the number in front of an independent variable. For example, if the regression equation is Y = mx + b then m is the regression coefficient of the x-variable. The regression coefficient estimates the effect of the independent variable(s) on the dependent variable. (Compare with Partial Regression Coefficients)
Regress On - The dependent variable is “regressed on” the independent variable(s). We will regress the cost of the space vehicle (based) on the weight of the vehicle. If x predicts y, then y is regressed on x. (i.e. Regress the dependent variable on the independent. Response variable is regressed on the explanatory variable.)
Rejection Region - The area in the tail(s) of the sampling distribution for a test statistic. The figure below shows the Rejection Region in red.
Residuals, Errors - The amount of variation on the dependent variable not explained by the independent variable.
Response Variable- Same as the independent variable.
Robust - Said of a statistic that remains useful even when one or more of the assumptions is violated.
S
Sample - A group of subjects selected from a larger group, the population.
Sample Statistic, Statistic - A measurement used to quantify a characteristic of the Sample. Even when the word sample is not used, the term statistic refers to the sample. Example: The sample mean is a measure of central tendency of the sample (see Population Parametric).
Sampling Error, Sampling Variability, Random Error - The estimation of the expected differences between the sample statistic and the population parameter.
Sampling Distribution - It is all possible values of a statistic and their probabilities of occurring for a sample of a particular size.
Scaling - expresses the centered observation in the units of the standard deviation of the observations.
Scatter Diagram, Scattergram, Scatter Plot - The pattern of points due to plotting two variables on a graph.
Significance - The degree to which a researcher’s finding is meaningful or important.
Significance Level - there are two types of significance levels, the observed significance level (alpha) and the chosen significance level (p-value). The lower the probability the greater the statistical significance, called alpha level.
Simple Linear Regression - A form of regression analysis, which has only one independent variable.
Slope - The rate at which the line or curve rises or falls when covering a given horizontal distance.
Spearman Correlation Coefficient (rho), Rank-Difference Correlation, rs. - A statistical measure of the amount of monotonic relationship between two variables that are arranged in rank order.
Specification error (Error, Specification) - A mistake made when specifying which model to use in the regression analysis. A common specification error involves including a irrelevant variable and leaving out an important variable.
Standard Deviation - A statistic that shows the square root of the squared distance that the data points are from the mean.
Standardized Measure of Scale - Any statistic that allows comparisons between things measured on different scales. Example: percent, standard deviations and z-scores
Standardized Regression Coefficient - Regression Coefficients which have been standardized in order to better make comparisons between the regression coefficients. This is particularly helpful when different independent variables have different units.
Standardized Regression Model - This is the regression model used after centering and scaling of the dependent variable and independent variables.
Standardized residuals - Standardized residuals are of the form (residual) / (square root of the Mean Square Error). Standardized residuals have variance 1. If the standardized residual is larger than 2, then it is usually considered large.
Standard Error, Standard Error of the Regression, Standard Error of the Mean, Standard Error of the Estimate - In regression the standard error of the estimate is the standard deviation of the observed y-values about the predicted y-values. In general, the standard error is a measure of sampling error. Standard error refers to error in estimates resulting from random fluctuations in samples. The standard error is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic. Typically the smaller the standard error, the better the sample statistic estimates of the population parameter. As N goes up, so does standard error.
Statistical Significance - Statistical significance does not necessarily mean that the result is clinically or practically important. For example, a clinical trial might result is a statistically significant finding (at the 5% level) that shows the difference in the average cholesterol rating for people taking drug A is lower than that of those taking drug B. However, drug A may only lower the cholesterol by 2 units more than drug B which is probably not a difference that is clinically important to the people taking the drug. Note: Large sample sizes can lead to results that are statistically significant that would otherwise be considered inconsequential.
Stepwise Regression - A method of regression analysis where independent variables are added and removed in order to find the best model. Stepwise regression combines the methods of backward elimination and forward selection.
Strength of Association, Strength of Effect Index - The degree of relationship between two (or more) variables. One example is R-squared, which measures the proportion of variability in a dependent variable explained by the independent variable(s).
Studentized Residuals: The studentized residual has the form of error/standard deviation of the error. Studentized residuals have constant variance when the model is appropraite.
T
Transformations - This is a method of changing all the values of a variable by using some mathematical operation.
U
Unbiased Estimator - A sample statistic that is free from systemic bias.
V
Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) - A statistics used to measuring the possible collinearity of the explanatory variables.
W
Weighted Least Squares - A method of regression used to take into account the non constant variance. The variables are multiples by a particular number (weights). It is typical to choose weights that are the inverse of the pure error variance in the response. (Minitab, page 2-7.) This choice gives large variances relatively small weights and visa versa.
Y
Y-intercept - is the point where a regressin line intersects the y axis.






